Remote digital content production
The remote production pilot activity aims to provide broadcasters with mechanisms to remotely produce content through 5G/6G networks, such as live events, which currently rely on dedicated networks or ad-hoc wired networks that are costly to deploy and lack versatility. Key components of the pilot include:
- MPE: Video Mixer/Switcher.
- vCE: Multimedia Content Understanding and Adaptation Engine.
- Optimization: Based on reinforcement learning and content analysis.
- Contribution: Through 5G (wireless) network.
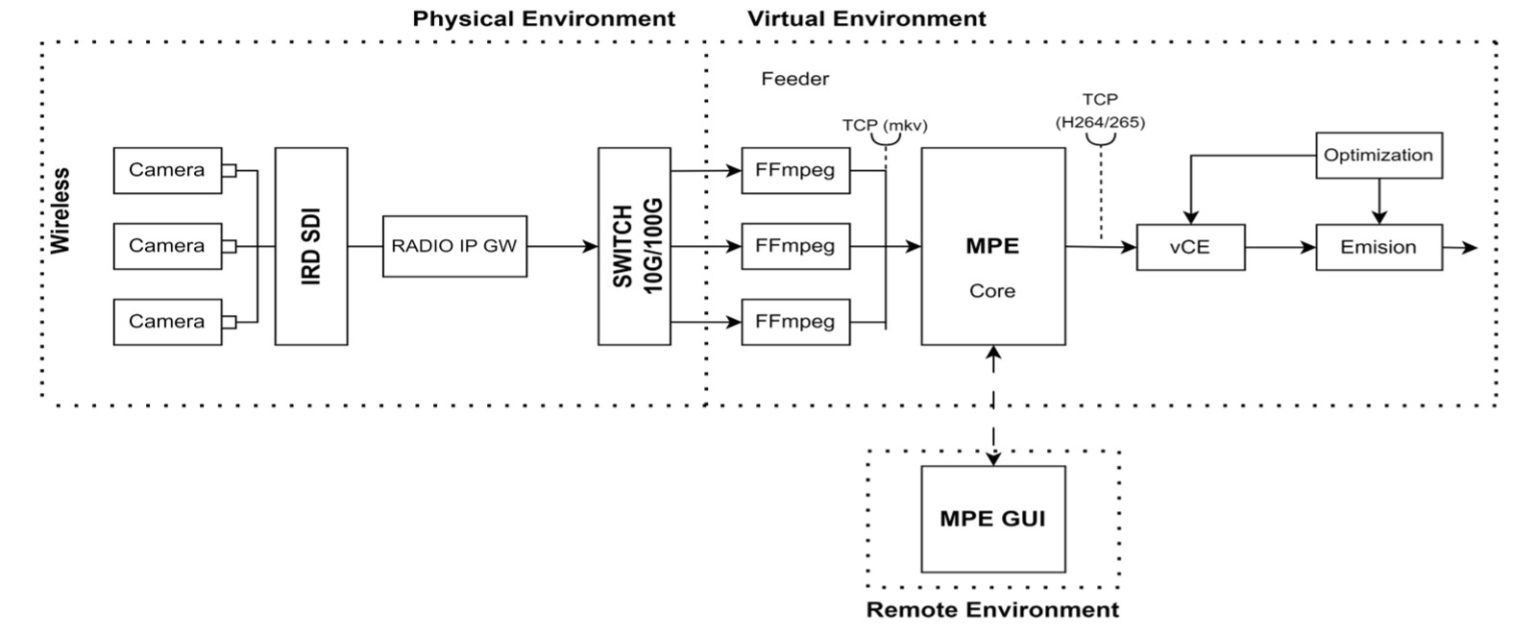
The pilot activity begins with defining the requirements and broadcasting systems in the following areas:
- Transmission: From the cameras capturing the information, whether connected to a 5G/6G modem or directly from a terminal.
- MEC of the Core Network: Near the radio access part to be used.
In the MEC part, the development of virtualized functions will be implemented to process the received multimedia signals (mixing, metadata tagging, encoding) and send them to the rest of the network with contribution quality, allowing further remote processing. To ensure quality, intelligent algorithms will be developed to configure the network capacity required by the services and optimize performance by processing at the edge of the network, as well as to measure the quality of the resulting signal. Finally, integration and functional validation tests will be conducted through a real field test to assess the pilot in real conditions and enhance its expected impact.
Preliminary Results
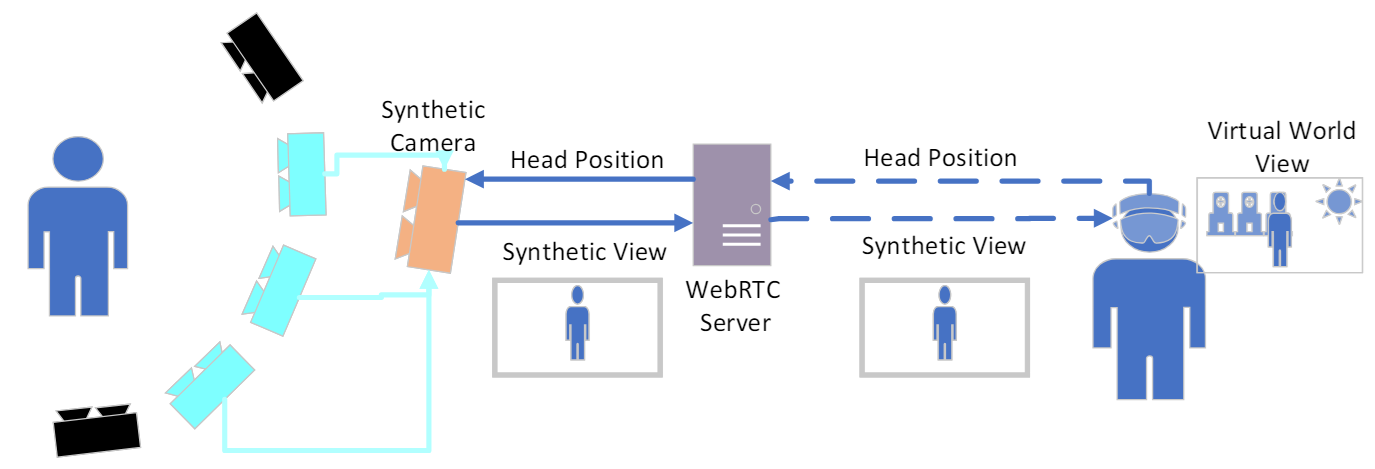
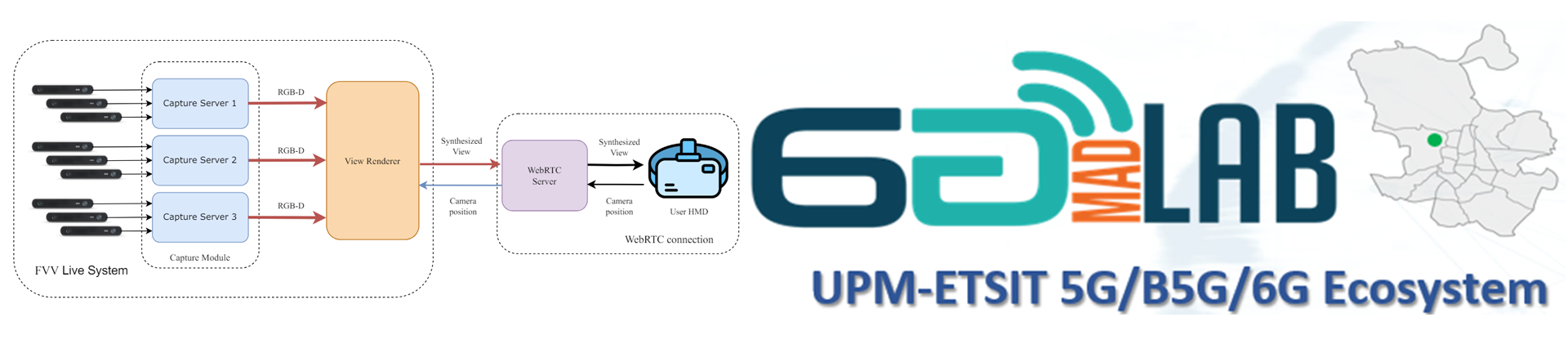
Untethered Real-Time Immersive Free Viewpoint Video
The recent development of new video capture systems has led to the adoption of volumetric video technologies to replace 2D video in use cases such as videoconference, where this enhancement promises to solve videoconference fatigue. In particular, volumetric capture allows the content to be viewed from different points of view, enabling more natural interaction during the videoconference. One of the solutions proposed for this scenario is Free Viewpoint Video (FVV). It makes use of a set of calibrated cameras that allows the use of real life information to generate a synthetic view from any arbitrary point in space. Although there are real-time capture developments of FVV systems, they make use of 2D displays and joysticks to control the point of view. In our opinion, this undermines the possibilities of volumetric video for the videoconferencing use case. Building on a previously developed FVV system, we present a novel untethered HMD-based immersive visualization system that enables point of view control with the user’s natural position and visualization of live volumetric content in a 3D environment. Synthetic views are generated in real-time by the FVV system, and streamed with low latency protocols to a Meta quest 3 HMD using a WebRTC-based server. This work discusses the architecture of the end-to-end system and describes the bitrate, framerate and latency values at which the system works.